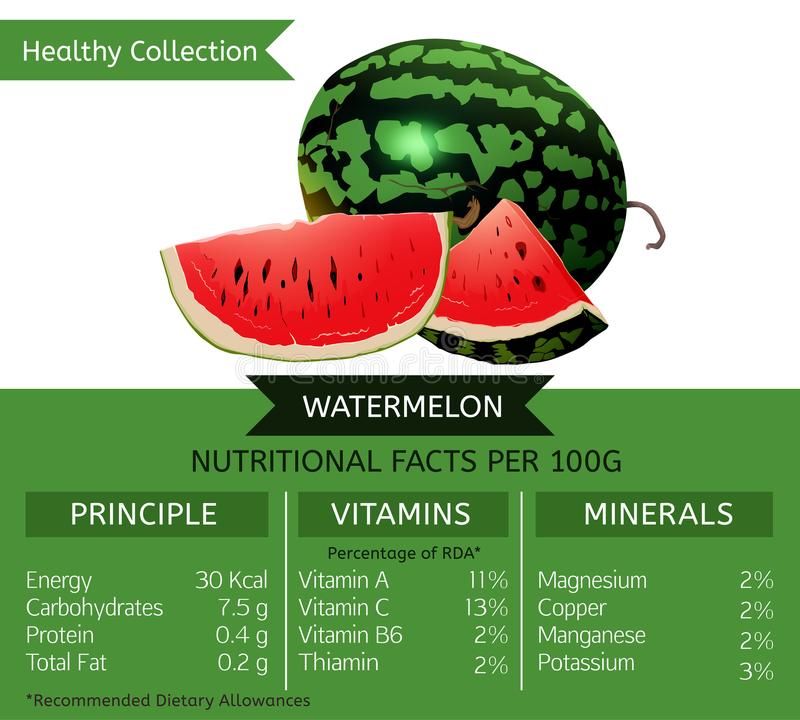
Watermelon is not only a refreshing and delicious summer treat, but it’s also packed with essential nutrients that can contribute to your overall health. This hydrating fruit is low in calories, high in vitamins, and offers a variety of health benefits. Here’s a breakdown of the nutritional facts of watermelon and how it can support your wellness:
1. Calories
Watermelon is incredibly low in calories, making it an excellent choice for those looking to maintain or lose weight. A typical 100-gram (3.5 oz) serving of watermelon contains just 30 calories. This makes it a great hydrating snack without adding many calories to your diet.
2. Water Content
Watermelon is aptly named, as it’s made up of about 90% water. This high water content not only makes it a hydrating fruit but also helps you feel full while consuming fewer calories. It’s especially refreshing during hot summer months when staying hydrated is crucial.
3. Carbohydrates
Watermelon provides 7.6 grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams, most of which come from natural sugars. The fruit contains a moderate amount of simple sugars, primarily glucose and fructose, which give watermelon its sweet taste. The carbohydrate content is relatively low compared to other fruits, making it a good option for those watching their carb intake.
4. Fiber
Each 100-gram serving of watermelon contains about 0.4 grams of fiber. While watermelon is not a high-fiber fruit, the fiber it does contain helps with digestion and contributes to satiety, keeping you feeling full longer.
5. Protein
Watermelon is not a significant source of protein. A 100-gram serving contains only 0.6 grams of protein. For a balanced diet, it’s best to pair watermelon with protein-rich foods like nuts, seeds, or yogurt.
6. Fat
Watermelon is very low in fat, with just 0.2 grams of fat per 100 grams. This makes it a heart-healthy choice that won’t contribute to your daily fat intake, especially when enjoyed in place of more calorie-dense snacks.
7. Vitamins and Minerals
Watermelon is rich in several vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin C: A 100-gram serving of watermelon contains about 8.1 milligrams of Vitamin C, which is about 10% of your daily recommended intake. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports immune health, helps with wound healing, and promotes healthy skin.
- Vitamin A: Watermelon is a good source of beta-carotene, a form of Vitamin A. This vitamin is essential for eye health, immune function, and maintaining healthy skin. The orange hue of the flesh near the rind indicates the presence of beta-carotene.
- Potassium: Watermelon provides 112 milligrams of potassium per 100 grams, which supports heart health, muscle function, and fluid balance in the body.
- Magnesium: This fruit also contains 10 milligrams of magnesium per 100 grams, a mineral important for muscle and nerve function, as well as bone health.
- B Vitamins: Watermelon contains small amounts of several B vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B5 (pantothenic acid), and B6 (pyridoxine). These vitamins play a role in energy production, brain function, and red blood cell formation.
8. Antioxidants
Watermelon is packed with antioxidants, particularly lycopene and beta-carotene. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that gives watermelon its red color and has been linked to a reduced risk of certain chronic diseases, including heart disease and some types of cancer. Lycopene is also known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce oxidative stress in the body.
9. Citrulline
Watermelon is a unique source of citrulline, an amino acid that is present in relatively high amounts in the rind. Citrulline has been shown to improve blood flow and may help reduce muscle soreness, making watermelon a popular post-workout snack. Some studies suggest that citrulline may also help support heart health by improving vascular function.
10. Watermelon’s Glycemic Index
Watermelon has a high glycemic index (GI), meaning it can cause a quick rise in blood sugar. However, its glycemic load (GL) is relatively low due to its high water content, meaning that eating watermelon in moderate amounts won’t significantly impact your blood sugar levels.
Health Benefits of Watermelon
Beyond its nutritional profile, watermelon offers a range of health benefits:
- Hydration: Due to its high water content, watermelon helps keep you hydrated, especially in hot weather or after physical activity.
- Digestive Health: The small amount of fiber in watermelon supports healthy digestion.
- Heart Health: Lycopene, potassium, and magnesium all contribute to cardiovascular health, helping to regulate blood pressure and improve circulation.
- Skin Health: The Vitamin A and Vitamin C content in watermelon supports healthy skin, promoting collagen production and reducing signs of aging.
- Muscle Recovery: The presence of citrulline in watermelon may help improve muscle recovery after exercise by promoting better blood flow and reducing muscle soreness.

Conclusion
Watermelon is a nutrient-packed fruit that provides a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants while being low in calories. Its high water content makes it an excellent hydrating snack, and its mix of vitamins and minerals supports overall health, including heart, skin, and digestive health. Whether you enjoy it on its own or incorporate it into fruit salads, smoothies, or desserts, watermelon is a delicious and refreshing way to stay healthy and hydrated.