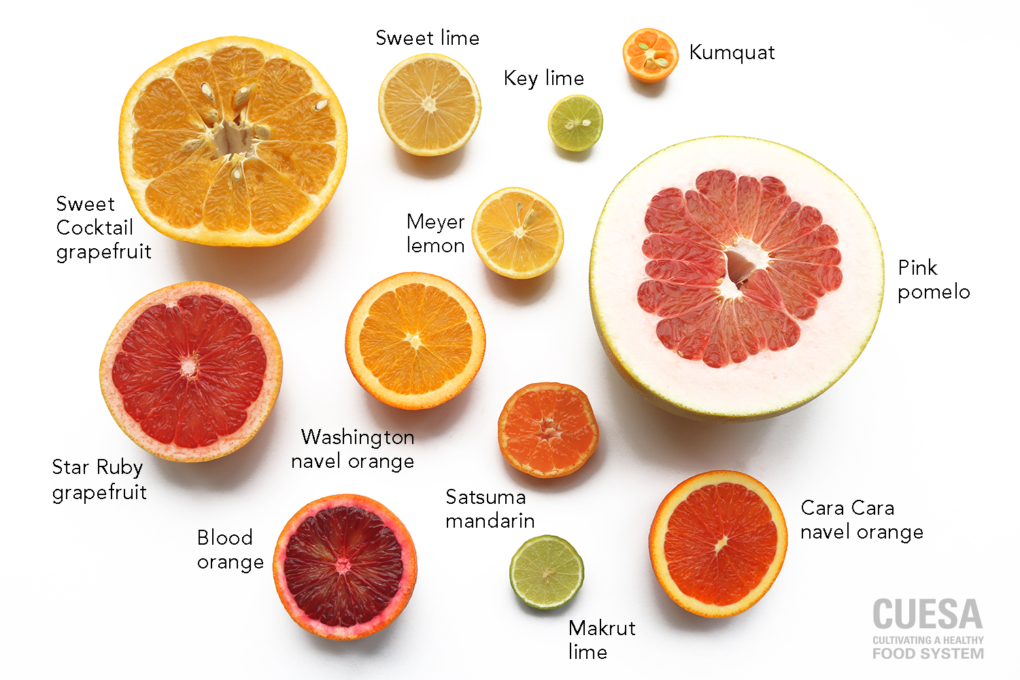
Citrus fruits are widely enjoyed for their refreshing taste and high vitamin C content, but not all oranges are created equal. While large citrus varieties like navel oranges and Valencia oranges are commonly seen in supermarkets, small orange fruits, such as mandarins, clementines, and tangerines, have a different appeal. These small fruits, often dubbed “easy peelers,” offer unique benefits and characteristics that set them apart from their larger counterparts. This article explores the key differences between small orange fruits and large citrus varieties in terms of taste, nutrition, appearance, and use.
1. Size and Appearance
The most noticeable difference between small and large orange varieties is, of course, their size. Large citrus fruits, such as navel or Valencia oranges, typically measure between 3 to 4 inches in diameter, making them bulky and substantial. They have a thick, dimpled skin that can require effort to peel. In contrast, small oranges, like mandarins and clementines, are compact, usually around 2 to 3 inches in diameter, with a thinner skin that is easier to peel, making them a convenient snack option.
2. Taste and Flavor Profile
One of the key distinctions between small and large citrus fruits is their flavor. Large oranges tend to have a sweet-tart balance, with a tangy note that can vary depending on the variety and ripeness. Navel oranges, for instance, are known for their mild sweetness, while Valencia oranges are typically more tangy, making them ideal for juicing.
On the other hand, small oranges generally lean more toward sweetness and are less tangy than their larger cousins. Mandarins, clementines, and tangerines are famous for their bright, sweet taste and minimal acidity. Their juicy, honey-like flavor makes them popular for snacking, especially with children. Small oranges, in general, offer a more consistent sweetness across their varieties, which is why they are often preferred for eating fresh or using in desserts.
3. Peelability and Convenience
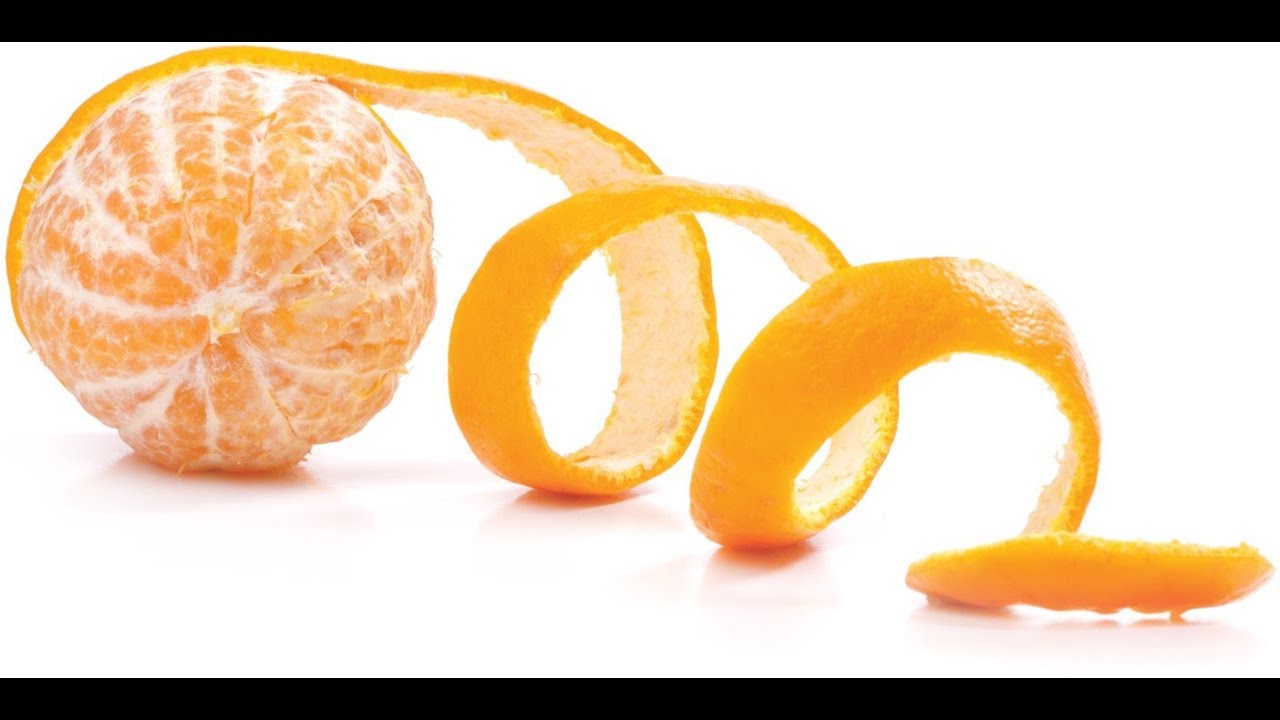

The ease of peeling is another major difference. Large oranges, while still peelable, tend to have a thicker, more textured skin that requires more effort to remove. Some varieties, like navel oranges, feature a “navel” that helps in peeling, but it can still be a challenge for those who want quick access to the fruit.
Small oranges, however, shine in terms of convenience. Varieties such as clementines and mandarins have a thin, segmented skin that peels off effortlessly. This ease of peeling, combined with the typically smaller size, makes them ideal for on-the-go consumption, especially for children or busy individuals. The segments of small oranges often come apart neatly, allowing for quick, mess-free snacking.
4. Nutrition and Health Benefits
When it comes to nutritional content, small and large oranges are quite similar, but there are some nuances. Both types are excellent sources of vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants. A medium-sized large orange can provide about 70 mg of vitamin C, roughly 80% of the daily recommended intake for adults.
Small oranges, despite their reduced size, are packed with comparable amounts of vitamin C and other nutrients. Since they are smaller, they may offer fewer calories per fruit, making them a great option for those looking for a lighter snack. They are also often consumed in higher quantities because of their convenient size, which means they can contribute a greater overall intake of beneficial nutrients.
Moreover, small oranges like clementines are often marketed as lower in calories and sugar, making them a popular choice for weight-conscious consumers. Their small, bite-sized portions help with portion control, and their high water content keeps you hydrated while providing a satisfying burst of sweetness.
5. Uses in Cooking and Culinary Applications
Both large and small citrus varieties have their place in cooking, but the way they are used can differ due to their size, taste, and peelability. Large oranges are often preferred for juicing, as their larger size yields more liquid. They are also frequently used in salads, marinades, sauces, and as garnishes due to their bright flavor and versatility.
Small oranges, on the other hand, are excellent for snacking, packing in lunchboxes, or adding a sweet note to fruit salads. The peel is thin enough to be used as a zest in baking, and their segments are ideal for incorporating into desserts, salsas, or garnishing cocktails. They are also favored for making jams, marmalades, and juices due to their intense sweetness.
6. Storage and Shelf Life
While both small and large citrus varieties have a relatively short shelf life, small oranges often have the edge in terms of convenience. Their smaller size and ease of handling make them easier to store and consume quickly, reducing waste. Large oranges, with their thicker skin, have a slightly longer shelf life when kept in the right conditions, but they may take up more space in the fridge or pantry.
Small citrus fruits like clementines and mandarins are also often sold in easy-to-transport crates or bags, making them convenient for families or individuals who prefer a quick, healthy snack. They’re usually sold in more compact packaging, contributing to their popularity in households with limited storage space.
7. Varieties to Know
When talking about small oranges, several well-known varieties stand out:
- Mandarins: These are small, sweet, and easy to peel. They are often seedless and have a bright, juicy flavor.
- Clementines: A type of mandarin, clementines are especially small, sweet, and often marketed as “cuties” or “halos.” They are a favorite for children and are sold in easy-to-open packaging.
- Tangerines: Similar to mandarins but slightly larger, tangerines are tangier and have a thicker skin that is still relatively easy to peel.
On the larger side, notable varieties include:
- Navel Oranges: Known for their sweet flavor and minimal seeds, navel oranges are great for eating fresh.
- Valencia Oranges: Primarily used for juicing, these oranges have a more tangy flavor and a higher juice yield than navel oranges.
Conclusion
small and large citrus fruits offer distinct advantages depending on the context of consumption. Large oranges are prized for juicing, versatility in cooking, and their balance of sweetness and tartness. Meanwhile, small oranges are favored for their convenience, sweeter flavor, and ease of peeling, making them ideal for snacking or adding a burst of sweetness to dishes. Whether you prefer the hearty juiciness of a large orange or the portable, honey-like sweetness of a small one, both types of citrus fruits contribute significantly to a healthy diet and provide refreshing, vitamin-packed options for any occasion.



